Data from: Is the Mediterranean the New Rio Grande? U.S. and E.U. Immigration Pressures in the Long Run
Data from: Is the Mediterranean the New Rio Grande? U.S. and E.U. Immigration Pressures in the Long Run
About this collection
- Extent
-
1 digital object.
- Cite This Work
-
Hanson, Gordon; McIntosh, Craig (2016). Data from: Is the Mediterranean the New Rio Grande? U.S. and E.U. Immigration Pressures in the Long Run. UC San Diego Library Digital Collections. https://doi.org/10.6075/J04M92GD
- Description
-
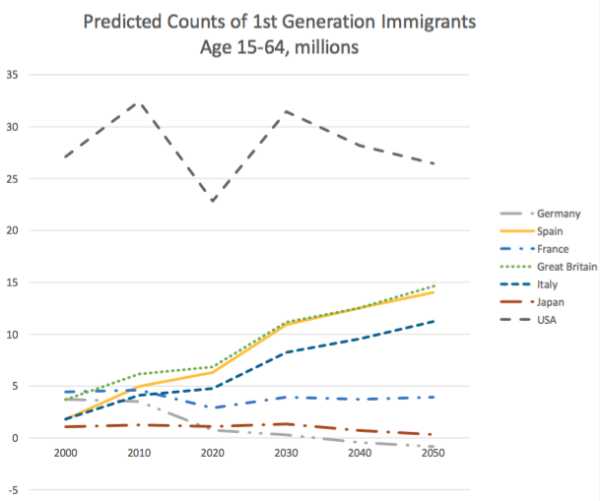
ABSTRACT: How will worldwide changes in population affect pressures for international migration in the future? We contrast the past three decades, during which population pressures contributed to substantial labor flows from neighboring countries into the United States and Europe, with the coming three decades, which will see sharp reductions in labor-supply growth in Latin America but not in Africa or much of the Middle East. Using a gravity-style empirical model, we examine the contribution of changes in relative labor-supply to bilateral migration in the 2000s and then apply this model to project future bilateral flows based on long-run UN forecasts of working-age populations in sending and receiving countries. Because the Americas are entering an era of uniformly low population growth, labor flows across the Rio Grande are projected to slow markedly. Europe, in contrast, will face substantial demographically driven migration pressures from across the Mediterranean for decades to come. While these projected inflows would triple the first-generation immigrant stocks of larger European countries, they would still absorb only a small fraction of the 800-million-person increase in the working-age population of Sub-Saharan Africa that is projected to occur over the coming 40 years.
- Creation Date
- 2016-01-01 to 2016-05-31
- Date Issued
- 2016
- Researchers
- Topics
Formats
View formats within this collection
- Language
- English
- Related Resources
- Hanson, Gordon; McIntosh, Craig (2016). Is the Mediterranean the New Rio Grande? U.S. and E.U. Immigration Pressures in the Long Run. Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 30, No. 4, pp. 57-82. https://doi.org/10.1257/jep.30.4.57
- Database on Immigrants in OECD Countries (DIOC): https://www.oecd.org/els/mig/databaseonimmigrantsinoecdcountriesdioc.htm
- UN World Population Prospects: https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/Download/Standard/Population/
Primary associated publication
Other resource
 Library Digital Collections
Library Digital Collections