Data from: Carbonic Anhydrases, EPF2 and a Novel Protease Mediate CO2 Control of Stomatal Development
Data from: Carbonic Anhydrases, EPF2 and a Novel Protease Mediate CO2 Control of Stomatal Development
About this collection
- Extent
-
1 digital object.
- Cite This Work
-
Engineer, Cawas B.; Ghassemian, Majid; Anderson, Jeffrey C.; Peck, Scott C.; Hu, Honghong; Schroeder, Julian I. (2015). Data from: Carbonic anhydrases, EPF2 and a novel protease mediate CO2 control of stomatal development. UC San Diego Library Digital Collections. https://doi.org/10.6075/J0TD9V7X
- Description
-
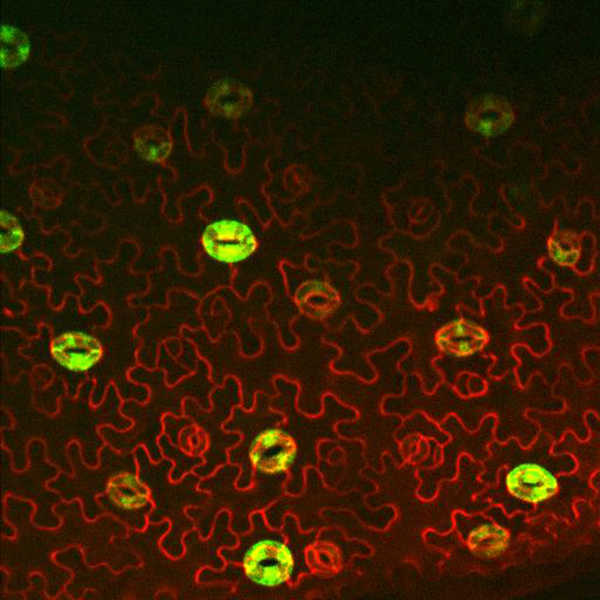
Data are deposited here from RNA-Seq transcriptomic experiments analyzing the Arabidopsis response to low and elevated carbon dioxide growing conditions. BAM, BAI and TDF files are uploaded from three independent biological replicates that we conducted for wild type and carbonic anhydrase mutant seedlings. Each set of replicates includes >1000 seedlings per sample and both genotypes were grown at low and elevated CO2 (hence 4 samples per set of replicates). Sampling was done at 5 days after germination to capture early signaling events as seedlings were adapting to the CO2 stimulus.
- Date Collected
- 2012 to 2013
- Date Issued
- 2015
- Research Team Head
- Researchers
- Scientific Names
- Topics
Formats
View formats within this collection
- Related Resources
- Engineer, C.B., Ghassemian, M., Anderson, J.C., Peck, S.C., Hu, H., and Schroeder, J.I. (2014) Carbonic anhydrases, EPF2 and a novel protease mediate CO2 control of stomatal development. Nature 513, 246-250. PubMed article: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25043023. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13452
- Raw data at NCBI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/?term=PRJNA218542
Primary associated publication
Source data
 Library Digital Collections
Library Digital Collections