Data from: The influence of a cross-reef channel on the wave-driven setup and circulation at Ipan, Guam
Data from: The influence of a cross-reef channel on the wave-driven setup and circulation at Ipan, Guam
About this collection
- Extent
-
1 digital object.
- Cite This Work
-
Clark, S. Jeanette; Becker, Janet M.; Merrifield, Mark A.; Behrens, James (2020). Data from: The influence of a cross-reef channel on the wave-driven setup and circulation at Ipan, Guam. UC San Diego Library Digital Collections. https://doi.org/10.6075/J01V5C9V
- Description
-
Currents, waves and water level observations from the field program of Clark et al. 2020 (https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JC015722).
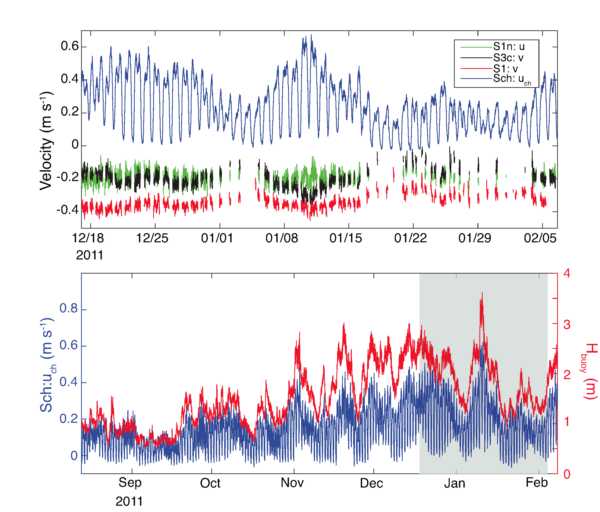
Abstract: The influence of a deep (30 m), narrow (30 m) cross-shore channel on the circulation and wave-induced setup over a shallow (~0.5 m) and wide (~400 m) shore-attached fringing reef is examined using field measurements collected at Ipan, Guam. Mean currents on the reef flat over a seven-week study period during mid and high tides when the reef is submerged are directed toward the channel with the alongshore component of the current increasing with proximity to the channel. The cross-shore component of the reef-flat current is directed onshore at the sensors in the far field of the channel with a weak offshore flow at the current meter located closest to the channel ~760 m to the north). Low-frequency fluctuations of the alongshore reef flat current and off-shore channel current are significantly correlated, and with the incident significant wave height. Mean and low frequency fluctuating currents are forced by the spatially variable wave-driven setup, modulated by tidal elevation, which creates a pressure gradient over the reef flat due to the channel where waves do not break. The dominant alongshore momentum balance on the reef flat is between the pressure gradient and bottom stress, with an inferred drag coefficient of CD~0.01. A simple analytical model is presented that is consistent with the observations and delineates the near- and far-field of the channel as a function of the aspect ratio of the reef. Observations from a longer deployment of channel currents are highly correlated with incident wave height in distinct tidal level bands. - Creation Date
- 2011 to 2012
- Date Issued
- 2020
- Authors
- Funding
-
This work was supported by the Army Corps of Engineers via both a subcontract from the University of California, San Diego (PO 1036151) and project W912HZ-14-2-0025, and by the National Science Foundation (OCE 0927407).
- Geographic
- Topics
Formats
View formats within this collection
- Language
- English
- Identifier
-
Identifier: Janet M. Becker: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2486-4095
- Related Resources
- Clark, S. J., Becker, J. M., Merrifield, M. A., & Behrens, J. (2020). The influence of a cross-reef channel on the wave-driven setup and circulation at Ipan, Guam. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 125, e2019JC015722. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JC015722
- The buoy wave data are available from the Coastal Data Information Program (CDIP, Station 121): https://cdip.ucsd.edu/m/products/?stn=121p1
- The Pago Bay wind data are available from the National Data Buoy Center (Station PGBP7): https://www.ndbc.noaa.gov/station_page.php?station=pgbp7
Primary associated publication
Source data
 Library Digital Collections
Library Digital Collections