Data from: A new method for diagnosing effective radiative forcing from aerosol-cloud interactions in climate models
Data from: A new method for diagnosing effective radiative forcing from aerosol-cloud interactions in climate models
About this collection
- Extent
-
1 digital object.
- Cite This Work
-
Duran, Brandon M.; Wall, Casey J.; Lutsko, Nicholas J.; Michibata, Takuro; Ma, Po-Lun; Qin, Yi; Duffy, Margaret L.; Debolskiy, Matvey; Medeiros, Brian (2024). Data from: A new method for diagnosing effective radiative forcing from aerosol-cloud interactions in climate models. UC San Diego Library Digital Collections. https://doi.org/10.6075/J0P26ZF1
- Description
-
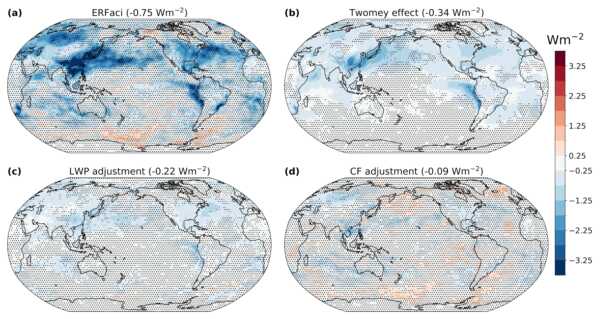
Aerosol-cloud interactions (ACI) are a leading source of uncertainty in estimates of the historical effective radiative forcing (ERF). One reason for this uncertainty is the difficulty of estimating the ERF from aerosol-cloud interactions (ERFaci) in climate models, which typically requires multiple calls to the radiation code and cannot disentangle the contributions from different process to ERFaci. Here, we develop a new, computationally efficient method for estimating the shortwave (SW) ERFaci from liquid clouds using histograms of monthly-averaged cloud fraction partitioned by cloud droplet effective radius (re) and liquid water path (LWP). Multiplying the histograms with SW cloud radiative kernels gives the total SW ERFaci from liquid clouds, which can be decomposed into contributions from the Twomey effect, LWP adjustments, and cloud-fraction (CF) adjustments. We test the method with data from five CMIP6-era models, using the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) satellite instrument simulator to generate the histograms. Our method gives similar total SW ERFaci estimates to other established methods in regions of prevalent liquid cloud, and indicates that the Twomey effect, LWP adjustments, and CF adjustments have contributed −0.34 ± 0.23, −0.22 ± 0.13, and −0.09 ± 0.11 Wm−2, respectively, to the effective radiative forcing of the climate since 1850 in the ensemble mean (95 % confidence). These results demonstrate that widespread adoption of a MODIS re– LWP joint histogram diagnostic would allow the SW ERFaci and its components to be quickly and accurately diagnosed from climate model outputs, a crucial step for reducing uncertainty in the historical ERF.
- Creation Date
- 2024
- Date Issued
- 2024
- Authors
- Funding
-
National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship, Grant No. DGE-2038238.
- Topics
Formats
View formats within this collection
- Language
- English
- Identifier
-
Identifier: Brandon M. Duran: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5427-8700
Identifier: Brian Mederios: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2188-4784
Identifier: Casey J. Wall: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7682-5576
Identifier: Margaret L. Duffy: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2206-2424
Identifier: Matvey Debolskiy: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9634-3627
Identifier: Nicholas J. Lutsko: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2733-7810
Identifier: Po-Lun Ma: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3109-5316
Identifier: Takuro Michibata: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1491-0297
Identifier: Yi Qin: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9045-8688
- Related Resources
- Duran, B. M., Wall, C. J., Lutsko, N. J., Michibata, T., Ma, P.-L., Qin, Y., Duffy, M. L., Medeiros, B., and Debolskiy, M.: A new method for diagnosing effective radiative forcing from aerosol-cloud interactions in climate models, EGUsphere [preprint], 2024. https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-2024-3063
- Duran, B. M., 2024: modis_cloud_radiative_kernels, Zenodo (code): https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13839355
- Image credit: Brandon Duran. "Ensemble results for the new method for diagnosing SW ERFaci."
Primary associated publication
Software
Collection image
 Library Digital Collections
Library Digital Collections